The Shanghai Academic Ranking of World Universities 2013
The Academic Ranking of World Universities (ARWU) is carried out by researchers at the Center for World-Class Universities of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (CWCU). The Center focuses on the study of world-class universities, delivering an annual database of main universities in the world, also providing consultation for government and universities.
Methodology
The methodology used by the Shanghai ranking has been contested and submitted to criticism for years. The reason why this is happening is the criteria used for acknowledging the universities and placing them in top 500: the privilege is given to research, leaving the performance in teaching aside. The selection of universities is based on criteria such as number of Nobel Laureates, Field Medalists (the Nobel of Mathematics), Highly Cited Researchers and published papers in Nature or Science, both Anglo-Saxon magazines. Moreover, the ranking includes universities whose scholars have provided a significant amount of papers to be indexed by Science Citation Index-Expanded (SCIE) and Social Science Citation Index (SSCI).
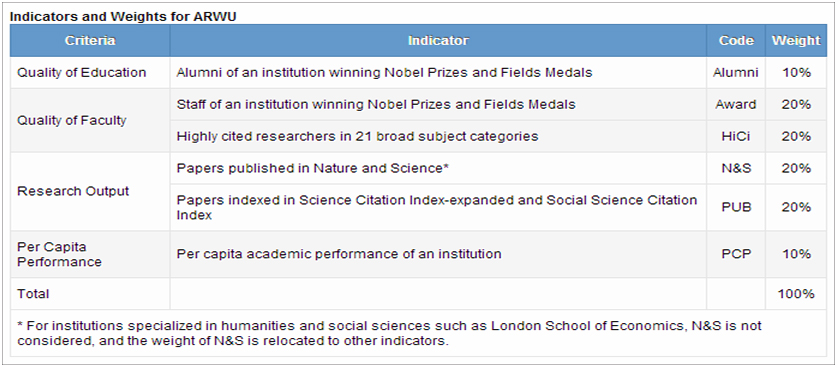
Ranking criteria and Weights
The indicators used to rank universities are based on academic and research performance. For each indicator, a score of 100 is assigned to the highest scoring institution, and the calculation for the other institutions is performed as a percentage of the top score. Data distribution for each indicator is examined to check possible distorting effects and every indicator is adjusted by using standard statistical techniques.
Indicators
The indicators used in the Shanghai ranking are the following:
- Alumni – (criterion: Quality of Education). The total number of the alumni that have won Nobel Prizes and Fields Medals. Different weights are set in accordance with the periods of obtaining degrees. Therefore, the weight is 100% for alumni who obtained degrees in 2001-2010, 90% for alumni obtaining degrees in 1991-2000, and so on until reaching the minimum of 10% which is given for alumni that have obtained degrees in 1911-1920. More degrees obtained by the same person does not account for more than one consideration in the ranking.
- Award – (criterion: Quality of Faculty). The total number of the staff of an institution winning Nobel Prizes in Physics, Chemistry, Medicine and Economics and Fields Medal in Mathematics. Weights are assigned in the same way as for the first indicator, according to time periods of winning the awards. In this respect, we have the weight of 100 % assigned to winners after 2011, 90% to winners in 2001-2010 and so on. If a winner is affiliated with more than one institution, each institution will receive the reciprocal of the number of institutions. If a Nobel Prize is shared by more than one person, weights are set according to the proportions of the prize for each person.
- HiCi – (criterion: Quality of Faculty). The total number of Highly Cited Researchers in 21 subject categories. If more than one affiliation exists for a Highly Cited Researcher, he/she is asked to estimate the weights for each affiliation. For researchers who do not provide an answer, the weights are calculated as following: 84% is given to the first affiliation and the rest of 16% is shared equally by the other affiliations (84% = average weight of the first affiliations for the researchers who answered).
- N & S – (criterion: Research output). Total number of papers published in Nature and Science in 2008-2012. The ranking takes into consideration only publications of “Article” and “Proceedings Paper” types.
- PUB – (criterion: Research output). Total number of publications included in Science Citation Index-Expanded (SCIE) and Social Science Citation Index (SSCI) in 2012. The publications are taken into account under the same criterion as above. A special weight of two has been introduced for papers that are indexed in SSCI.
- PCP – (criterion: Per Capita Performance). Defined as the weighted scores of the other five indicators divided by the number of full-time equivalent academic staff.
Having set the indicators and measured weights, the top 500 has been finalized. The results show Harvard University on the first place, setting the trend for American universities in the top. In top 20, only 2 countries have entered, the rest of 17 positions being dominated by American institutions: UK with University of Cambridge on 5th place and University of Oxford on the 10th and Switzerland on the 20th place with Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich. Top 3 countries with the biggest number of positions occupied in top 500 world-class universities are:
- USA – 146 institutions
- Great Britain – 37 institutions, on the same position as Germany – 37 institutions
- China – 34 institutions
The Shanghai Academic Ranking of World Universities is widely submitted to criticism and in some respects, disbelief, due to the methodology used. Several pieces of analysis have been conducted to verify the accuracy of the ranking, and results have shown in many cases that the indicators used are not relevant and that the methodology does not lack several major problems. Nevertheless, this is the most viewed top in the world, whether it is for approval, reference or criticism.
Reference:
Image source:

Tags: Education and Training performance, Performance Measurement, The Academic Ranking of World Universities