Preparing for the future: why businesses should build organizational resilience

Image Source: Gerd Altmann | Pixabay
Today’s fast-paced and rapidly changing business environment is characterized by uncertainty and the interdependence of economies, societies, and markets. Thus, organizations are facing numerous challenges that can threaten their ability to survive and thrive. According to the Harvard Business Review, the key forces stressing the business landscape include the pandemic and geopolitical instability along with other factors, such as technological disruption, climate change, and globalization. Unsurprisingly, given these difficulties, business leaders decided to focus on organizational resilience in order to adapt to this dynamic environment, leverage opportunities, and deliver sustainable performance improvement.
In a report from Cranfield School of Management, Professor David Denyer defines organizational resilience as the ability of an entity to anticipate, prepare for, respond to, and adapt to incremental change and sudden disruptions to survive and prosper. His paper underlines the idea that organizational resilience requires special control over multiple independent and redundant layers of protection for all critical assets (people, products, property, information) and compliance (standard operating procedures, processes, and training).
Organizations can increase their resilience by adopting various frameworks and models (see Figure 1).

Figure 1 – Resilience Frameworks and Models | Sources: Adapted from Hepfer and Lawrence, 2022; International Organization for Standardization, 2019; The National Institute of Standards and Technology, n.d.; The International Consortium For Organizational Resilience, n.d.; Armour, n.d.; Tanner, Prayag, and Kuntz, 2022
To increase resilience, organizations should develop capabilities, competencies, and principles that are aligned with their chosen resilience framework or model. Some of the capabilities and competencies that can enhance resilience include leadership commitment, risk management, business continuity planning, incident response planning, communication, training, and awareness, according to Stephanie Duchek’s article from 2019. In addition, the six principles stated by Harvard Business Review for enhancing organizations and decision processes to become more resilient can be consulted (see Figure 2).
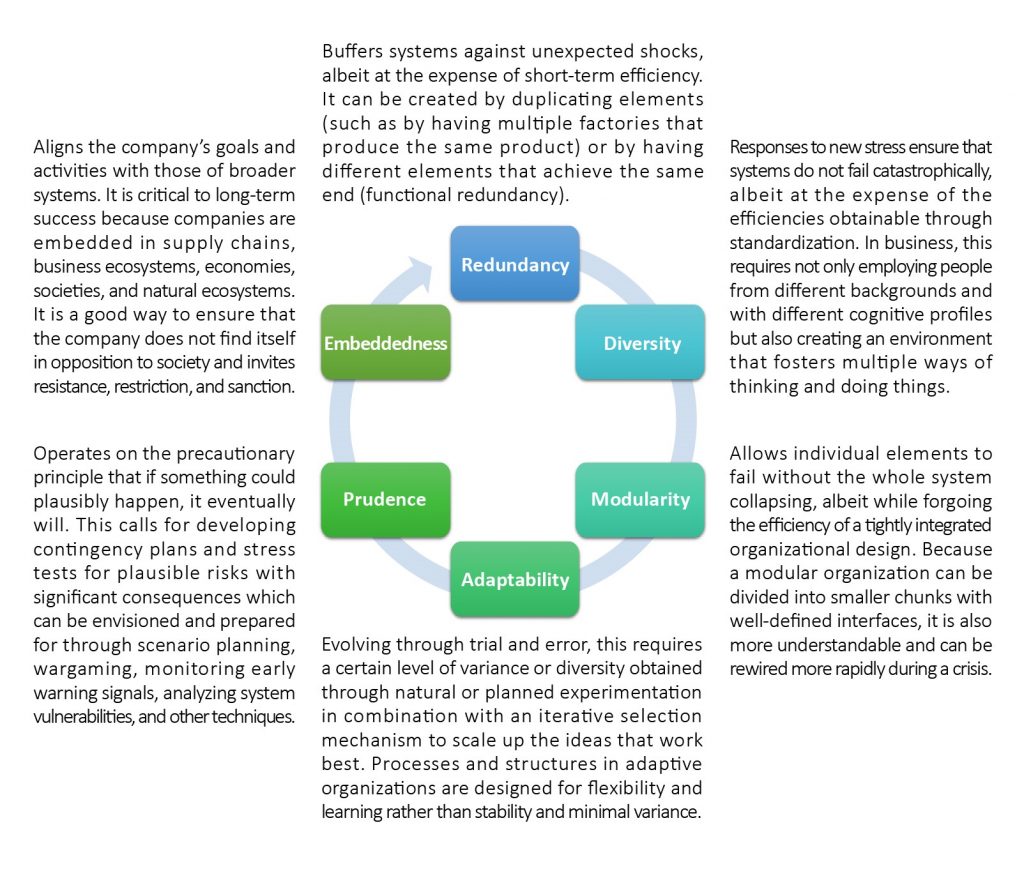
Figure 2 – The 6 principles for increasing resilience of long-lasting systems| Source: Adapted from Harvard Business Review 2020 Article
The International Consortium For Organizational Resilience (ICOR), a global consortium of business continuity and resilience professionals, developed a model based on ISO 22316. The model is composed of three dimensions (leadership & strategy, preparedness & managerial risk, and culture & behavior) with nine strategies directly subordinated to them and six sets of corresponding behaviors. One benefit of the ICOR model is its structured approach to resilience management, which can help organizations better understand their vulnerabilities and develop more effective risk mitigation and response plans. The model also emphasizes the importance of ongoing evaluation and improvement of resilience plans, which can help organizations stay ahead of evolving threats.
There are some limitations to the ICOR model that may not be suitable for all types of organizations— particularly smaller or less complex ones—because, in comparison with big enterprises, most SME owners do not have access to resilience training and tools or their employees are not involved in the development of strategies to increase an entity’s resilience, as stated by the International Labour Organization. Additionally, the model may not adequately account for potential cascading or interdependent risks.
Despite its limitations, the ICOR model is widely used to measure resilience in a variety of industries, including healthcare, transportation, and manufacturing. It is important to mention that this model is not used in most cases by itself, but rather in combination with one or more frameworks or models mentioned above, depending on the needs and the industry in which the organization operates.
To thrive in today’s tumultuous business environment, organizations must develop the capabilities and competencies necessary to anticipate, prepare for, and respond to disturbances effectively.

